Whatever you call it, don’t let the name fool you. These are not the manufactured homes you are used to hearing about but represent a building technique trend that has been adopted by several construction industry leaders as an alternative to traditional on-site construction methods.
There are several advantages to this technique. The indoor controlled manufacturing environment and material staging allow for a higher level of precision and less waste during the manufacturing process. It allows construction to happen without weather delays and provides safer working conditions for employees. Despite its prefabricated construction, building structures can be configured to just about anything, using the same materials and designing to the same codes and standards as traditional construction.
The true gem of prefabricated construction lies in its ability to streamline the construction process and produce buildings in a fraction of the time compared to conventional construction.
What is Modular Construction?
Yes
- Perfect for businesses that need to get their building up and running without the long build times of traditional construction.
- Made up of modules that are prebuilt in a factory-controlled setting then transported and quickly assembled on location.
- Code compliant buildings constructed out of individual, prefabricated sections.
- More sustainable than traditional construction due to the efficient construction schedule and reduction of material waste during the construction process.
- Similar to traditional construction, virtually endless configurations and design options can be built to replicate the same look, using the same materials as traditional construction.
No
- Mobile Office Trailers
- A cheap alternative to traditional construction
- Built with sub-par materials
- Rest on top of a wheels and chassis trailer base
- Built for short-term life spans
Common Uses
Factory Built facilities can be tailored to fit your needs, and a wide range of industries use them. Some of the industries and more common uses include:
- Administrative — temporary sales office
- Agriculture — office space
- Construction — stackable offices, mobile offices, job site offices
- Healthcare — hospitals, clinics, dentist offices, training centers, laboratory space, record storage
- Financial — kiosks and bank buildings
- Education — classrooms, day cares, school add-ons, cafeterias, lobbies
- Retail — coffee shops, offices, sales offices, etc.
- Religious — churches, assemblies, schools, meeting and storage space
- Transportation — bus stations, gas stations, convenience stores
- Government — military, parks and recreation, post offices, public safety
- Specialty — anything and everything outside of a normal scope building
Types of Modular Construction Buildings
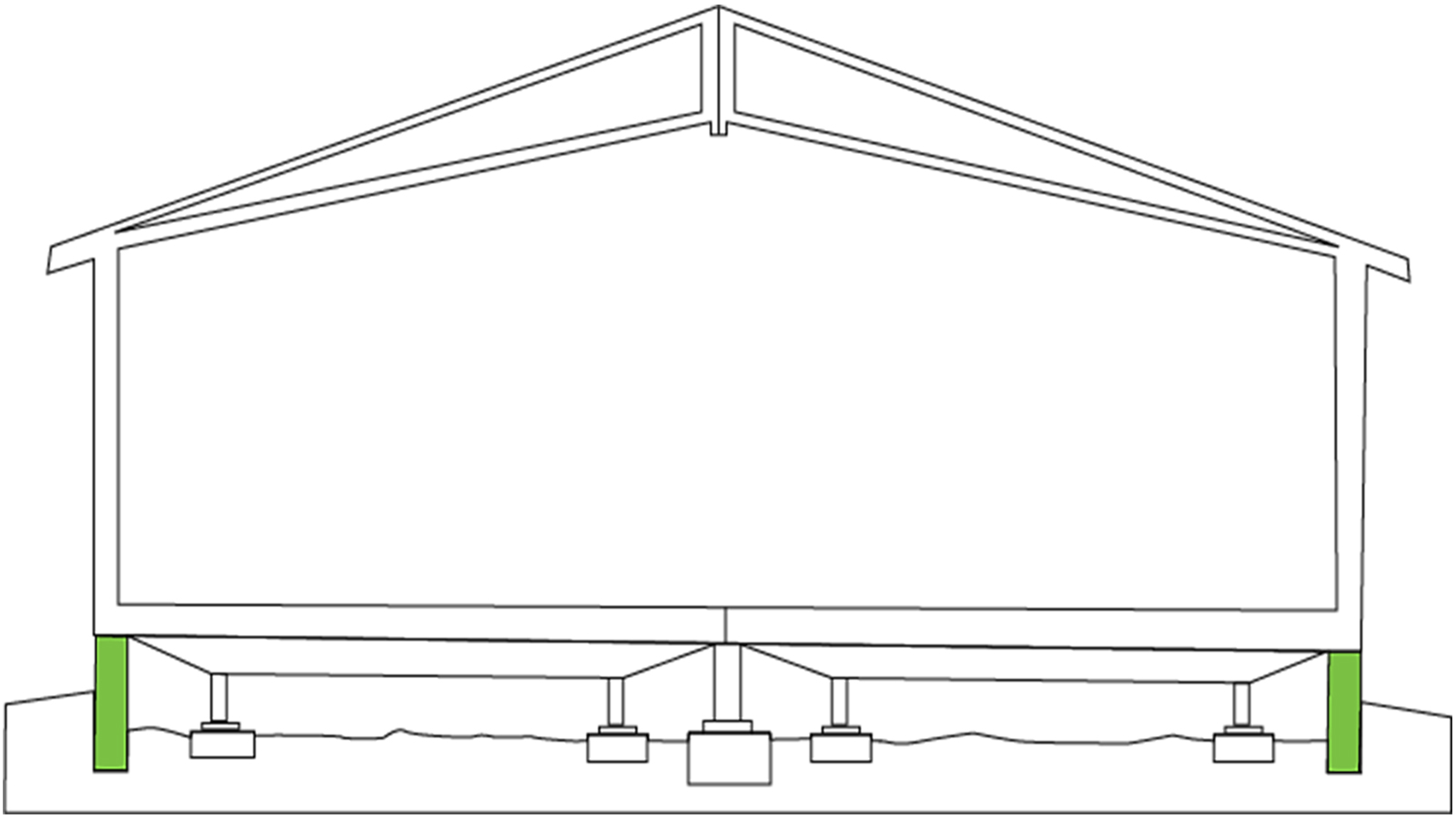
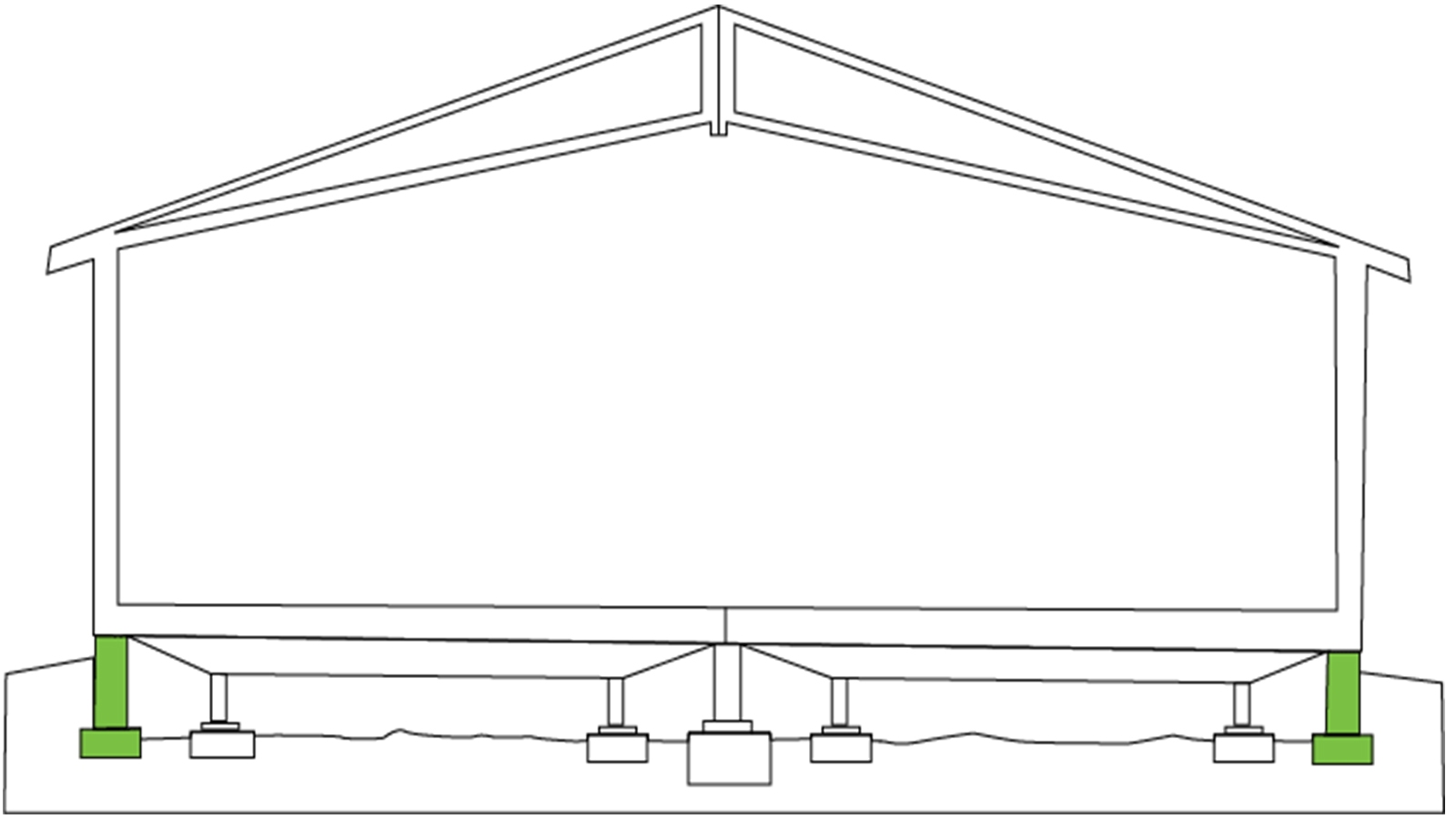
There are two types of factory built buildings, permanent and temporary, that are defined by their foundation. Here are a few questions you should ask yourself to determine which type of modular building is right for you:
Permanent
Permanent factory built buildings follow the same modular building process and sit on a permanent stem wall or concrete foundation. Businesses that are planning for a long-term stay at a fixed location are best suited for permanent prefabricated construction (i.e. Healthcare and K-12 educational facilities).
Temporary
These buildings also follow the same factory built building process but sit on a more temporary foundation for ease of building relocation. Businesses that are planning a more temporary stay at their current location are best suited for a temporary foundation (i.e. construction offices).
Cost of Modular Construction
It is important for us to be transparent with our customers about how we price their buildings. Below are just a few factors that we consider when appraising the cost of constructing a factory built building:
Modular Construction Standard Specs
Width
Federal and State highway regulations limit the maximum vehicle cargo width size to 8ft. Therefore, it is typical to obtain highway permits which allow for carrying wider loads. The common sizes range from 12 feet to 14 feet wide but can go up to 16 feet in width, depending on the project.
Length
Federal and State highway regulations limit vehicle cargo lengths to 8 feet. Modern buildings range from 16 to 64 feet in length but can go up to 70 feet in length depending on local regulations.
Height
Federal and State highway regulations limit vehicle cargo height to 14 feet. Modern’s average module height is 15 feet but can go up to 16 feet high, upon permit approvals.
Design
Factory built buildings can be customized to match just about anything a client may have in mind. Involving an architect in more complex projects is recommended.
Exterior
Exterior finishes are constructed using the same top quality material that is utilized in conventional buildings.
Interior
Interior finishes are constructed using the same top quality material that is utilized in conventional buildings.
Foundation
Materials utilized in foundations for factory built buildings depend on soil compaction and site conditions. The most common foundations are stem wall and post and beam foundations, which are similar to what you would find in a site-built structure.

